Introduction
Why Patenting a Website Idea is Crucial
In today’s digital age, your website idea could be the next big thing. But without a patent, your groundbreaking concept is open for anyone to copy. Securing a patent protects your intellectual property, giving you exclusive rights to your idea and a competitive edge in the market. Trust us, you don’t want to skip this step; it’s like putting a lock on your treasure chest!
Common Misconceptions About Patenting Digital Ideas
Many people think that patents are only for physical inventions, but that’s far from the truth. Digital ideas, including website concepts, can also be patented. However, the process can be complex and requires a thorough understanding of patent laws. So, let’s bust this myth and get you the protection your idea deserves.
Scope of This Article
This article aims to guide you through the intricate process of patenting a website idea. From understanding intellectual property rights to filing the patent application, we’ll cover it all. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear roadmap for patenting your website idea and safeguarding your intellectual property. So, are you ready to take this journey with us? Let’s dive in!
Understanding Intellectual Property Rights
Types of Intellectual Property: Copyright, Trademark, Patent
Intellectual Property (IP) is a broad term that covers various types of protections for your creative works. These include copyrights, trademarks, and patents. While copyrights protect the expression of an idea (like a blog post or a song), trademarks protect brand names and logos. Patents, on the other hand, protect new inventions or discoveries. Understanding the differences between these can help you decide the best way to protect your website idea.
What Can and Cannot Be Patented
When it comes to patenting a website idea, it’s crucial to know what qualifies for a patent and what doesn’t. In general, abstract ideas, natural phenomena, and laws of nature cannot be patented. However, if your website idea involves a unique process, system, or software, it could be eligible for a patent. The key is that the idea must be new, non-obvious, and useful. So, before you jump into the patenting process, make sure your website idea meets these criteria. Otherwise, you might be setting yourself up for disappointment.
Preliminary Steps Before Applying for a Patent
Conducting a Patent Search
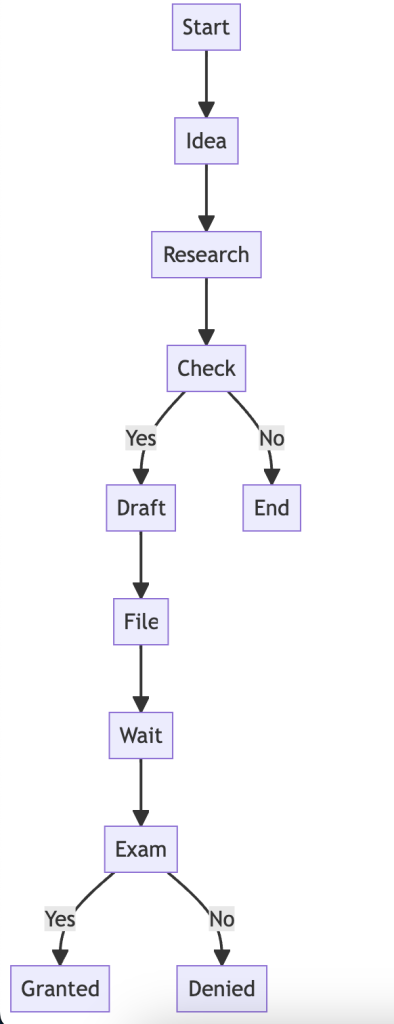
Before you even think about applying for a patent, it’s crucial to conduct a thorough patent search. This will help you determine if your website idea is truly unique or if someone else has already patented something similar. There are various online databases and tools available for this, and you can also hire professionals to do it for you. A comprehensive patent search can save you time and money in the long run.
Documenting Your Website Idea
Documentation is key when it comes to patenting. You’ll need to create a detailed record of your website idea, outlining how it works, its features, and its functionalities. This should include sketches, flowcharts, and even code if applicable. The more detailed your documentation, the stronger your patent application will be. It’s like laying down the foundation for a house; the stronger it is, the more secure the entire structure will be.
Consulting a Patent Attorney
Navigating the patent process can be complex and time-consuming. That’s why it’s often recommended to consult a patent attorney. They can guide you through the legal maze, helping you avoid common pitfalls and ensuring that your application is as strong as possible. Investing in professional advice at this stage can pay off significantly in terms of securing a robust patent.
Taking these preliminary steps seriously can set you up for success in the patenting process. It’s all about doing your homework and getting the right advice. Trust us, your innovative website idea is worth it!
Preparing Your Patent Application
Components of a Patent Application
A patent application is more than just a form; it’s a comprehensive document that needs to cover several key components. This includes a title, abstract, detailed description, claims, and any relevant drawings or diagrams. Each of these elements serves a specific purpose in demonstrating the uniqueness and functionality of your website idea. Understanding the importance of each component can make or break your application.
Creating a Detailed Description and Drawings
The heart of your patent application lies in its detailed description and any accompanying drawings. This is where you lay out the mechanics of your website idea, explaining how it works, what it does, and why it’s innovative. The description should be so thorough that someone in the same field could replicate your idea just by reading it. The drawings, if applicable, should be clear, labeled, and directly related to the description.
Claims: Defining the Scope of Your Patent
The claims section is arguably the most critical part of your patent application. This is where you define the boundaries of what your patent will protect. In other words, you’re stating what aspects of your website idea are actually new and should be protected by law. Crafting precise and broad claims can be a delicate balancing act, but it’s essential for protecting your intellectual property effectively.
Filing the Patent Application
Types of Patent Applications: Provisional vs. Non-Provisional
Deciding between a provisional and a non-provisional patent application is a pivotal choice. A provisional application is like a placeholder, giving you a year to develop your idea further and file a non-provisional application. It’s less expensive but doesn’t grant you a patent. On the other hand, a non-provisional application is more complex and starts the official examination process. Your choice will depend on the stage of your idea’s development and your budget.
Filing Process: Online vs. Paper
In today’s digital age, filing a patent application online is generally quicker and more efficient. However, some people still prefer the traditional paper filing method. Both have their pros and cons, but online filing often speeds up the process and allows for easier tracking. Choosing the right filing method can save you both time and headaches down the line.
Costs Involved in Filing a Patent
Filing a patent isn’t cheap, and it’s crucial to budget for this. Costs can include filing fees, attorney fees, and potential maintenance fees down the road. These costs can vary widely depending on the complexity of your patent and the country in which you’re filing. Being aware of these costs upfront can help you make an informed decision and avoid any nasty surprises later.
In conclusion, filing a patent application is a significant step that involves several important decisions and costs. It’s not just a matter of filling out some paperwork; it’s a strategic move to protect your intellectual property. So, make sure you understand each aspect thoroughly before diving in.
The Examination Process
First Examination Report (FER)
After you’ve filed your patent application, the patent office will conduct an initial review and issue a First Examination Report (FER). This report outlines any objections or questions the examiner has about your application. Understanding the FER is crucial, as it sets the stage for the rest of the examination process.
Responding to Objections
Receiving objections on your patent application isn’t the end of the world; it’s a normal part of the process. You’ll have a set period to respond to these objections, usually by amending your application or providing additional information. How well you respond can make or break your application, so consider consulting a patent attorney for this step.
Amending Your Application
If the patent examiner has objections, you’ll likely need to amend your application. This could involve clarifying your claims, providing additional data, or even narrowing the scope of your patent. Amendments are a delicate balance; you don’t want to weaken your patent, but you also need to overcome the examiner’s objections.
Post-Approval Steps
Maintaining Your Patent
Congratulations, your patent has been approved! But the journey doesn’t end here. You’ll need to pay maintenance fees at regular intervals to keep your patent active. Failure to do so can result in your patent being declared ‘lapsed,’ and you could lose your exclusive rights. It’s essential to mark these due dates on your calendar and budget for them.
Enforcing Your Patent Rights
Having a patent is one thing; enforcing it is another. If you discover that someone is infringing on your patent, it’s your responsibility to take legal action. This often involves sending a cease-and-desist letter followed by potential litigation. It’s crucial to consult with a patent attorney to understand your options and the best course of action.
Post-approval, the focus shifts from obtaining rights to maintaining and enforcing them. Both steps are critical for leveraging your patent to its full potential. Being vigilant about maintenance fees and potential infringement can help you make the most of your hard-earned patent.
Cost and Timeline Table for Patenting a Website Idea
| Step | Description | Duration | Cost Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Conduct a Patent Search | 1-2 weeks | $0-$500 |
| 2 | Consult a Patent Attorney | 1 week | $200-$500 |
| 3 | Draft a Provisional Patent Application | 2-4 weeks | $1,000-$3,000 |
| 4 | File the Provisional Patent Application | 1 day | $70-$280 |
| 5 | Develop the Website Idea | 3-6 months | Varies |
| 6 | Draft a Non-Provisional Patent Application | 4-8 weeks | $5,000-$15,000 |
| 7 | File the Non-Provisional Patent Application | 1 day | $400-$1,200 |
| 8 | Respond to USPTO Office Actions (if any) | 3-6 months | $1,000-$3,000 |
| 9 | Wait for Patent Examination | 1-3 years | $0 |
| 10 | Pay Issue and Maintenance Fees | N/A | $1,000-$4,000 |
| 11 | Launch and Monetize the Website | Varies | Varies |
| Total | $9,670-$27,480 |
Note: The durations and cost estimates are approximate and can vary based on complexity, attorney fees, and other factors. Always consult with professionals for the most accurate advice.
Special Considerations for Website Ideas
Software Patents and Their Relevance to Website Ideas
When it comes to website ideas, the waters get a bit murky. Software patents are a hot topic in the intellectual property world, and they directly impact the patentability of website ideas. It’s crucial to understand that not all aspects of a website can be patented. For example, general features like “a user login system” might not be unique enough for a patent. However, if your website idea involves a novel algorithm or a unique user interface, you may have a stronger case for patenting.
FAQs
Is it Worth Patenting a Website Idea?
The million-dollar question: is it worth it? Patenting a website idea can be a significant investment in terms of time, effort, and money. However, if your idea is genuinely innovative and has commercial potential, securing a patent can offer a competitive edge. It provides you with exclusive rights to your idea, preventing others from copying or using it without your permission.
How Long Does the Patent Process Take?
Patience is a virtue, especially in the patent world. The duration of the patent process can vary widely, often taking anywhere from 18 to 36 months. This timeline can be influenced by various factors, including the complexity of your idea and the backlog at the patent office.
What Happens if Someone Infringes on My Patent?
Infringement is a serious matter. If someone uses your patented idea without permission, you have the legal right to take action. This could range from sending a cease-and-desist letter to filing a lawsuit. The key is to act swiftly and consult with a patent attorney to determine the best course of action.
Can I Sell or License My Patent?
Your patent is an asset. Once you’ve secured a patent, you have the option to license it to others or even sell the patent outright. This can be a lucrative way to monetize your idea without having to build and market a website yourself.
Conclusion
Recap: The Importance and Process of Patenting a Website Idea
Let’s circle back to where we started. Patenting a website idea is not just a bureaucratic formality; it’s a strategic move to protect your intellectual property and secure a competitive edge in the marketplace. From understanding different types of intellectual property rights to navigating the complex patent application process, we’ve covered a lot of ground. Securing a patent can be a game-changer, offering you exclusive rights and potentially high returns on your innovative idea.
Next Steps: Turning Your Patented Idea into a Reality
So, you’ve got a patent. What now? The journey doesn’t end with a patent approval. It’s time to turn that patented idea into a tangible product or service. Whether you decide to develop it yourself, license it to others, or sell the patent outright, the next steps are crucial. Consult experts, build a team, and create a business plan to bring your patented website idea to life.
In conclusion, patenting a website idea is a multifaceted process that requires careful planning, timely execution, and ongoing maintenance. But the rewards can be immense, offering you not just legal protection but also a pathway to commercial success. Your idea could be the next big thing, and a patent could be the key to unlocking its potential.



